Comparison of Environmental Impact of Plastic, Paper and Cloth Bags
This Briefing Note looks at the environmental impact of different types of carrier bags- cloth, paper and plastic. Their impact is compared based on two categories: decomposition and their recyclability.
1. Decomposition
Paper Bags Research demonstrates that paper in landfills does not degrade or break down at a substantially faster rate than plastic does. In fact, nothing completely degrades in modern landfills because of the lack of water, light, oxygen and other important elements that are necessary for the degradation process to be completed. A paper bag takes up more space than a plastic bag in a landfill, but because paper is recycled at a higher rate, saving space in landfills is less of an issue.
Plastic Bags It can take between 400 and 1000 years for plastic bags to decompose. A number of UK retailers have recently introduced degradable carrier bags. These bags are made from plastic which degrades under certain conditions or after a predetermined length of time. There are two types of degradable plastic: bio-degradable plastics, which contain a small percentage of non oil-based material, such as corn starch; and photodegradable plastics, which will break down when exposed to sunlight.
2. Recyclability
Paper Bags It takes 91% less energy to recycle a pound of plastic than it takes to recycle a pound of paper.
A report on the production of carrier bags made from recycled rather than virgin polythene concluded that the use of recycled plastic resulted in the following environmental benefits:
· reduction of energy consumption by two-thirds · production of only a third of the sulphur dioxide and half of the nitrous oxide · reduction of water usage by nearly 90% · reduction of carbon dioxide generation by two-and-a-half times
A different study concluded that 1.8 tonnes of oil are saved for every tonne of recycled polythene produced.
Cloth Bags Cloth Bags can be recycled like most textiles. Textile recovery:
· Reduces the need for landfill space. Textiles present particular problems in landfill as synthetic (man-made fibres) products will not decompose, while woollen garments do decompose and produce methane, which contributes to global warming. · Reduces pressure on virgin resources. · Aids the balance of payments as we import fewer materials for our needs. · Results in less pollution and energy savings, as fibres do not have to be transported from abroad.
Plastic Bags
Some supermarkets offer recycling banks instore.18 They can be recycled into many different products or can be repossessed into small pellets, or post consumer resin, which can become feed stock for a variety of products such as new bags, pallets, containers, crates, and pipe.
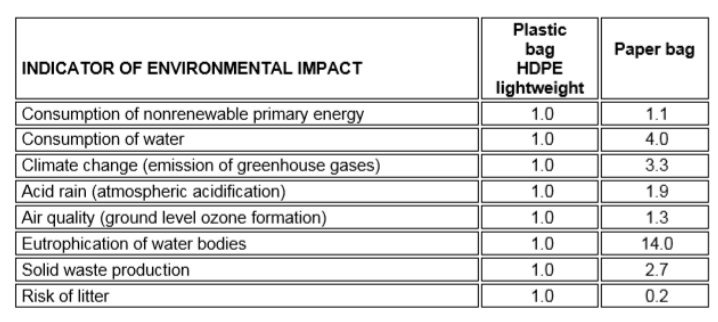
Environmental Impact of Plastic vs. Paper Bags
In 2005, the Scottish Government issued a full environment impact assessment report on the effects of a proposed plastic bag fee20. The Report contains the comparison between plastic and paper bags, outlined in the table below. The lightweight plastic bag was given a score of 1 in all categories as a reference point. A score greater than 1 indicates that a paper bag makes more contribution to the environmental problem than a lightweight plastic bag when normalised against the volume of shopping carried. The indicators take account of emissions which occur over the whole lifecycle.